ReactFlow Node Intersections: Advanced Edge Routing and Collision Detection
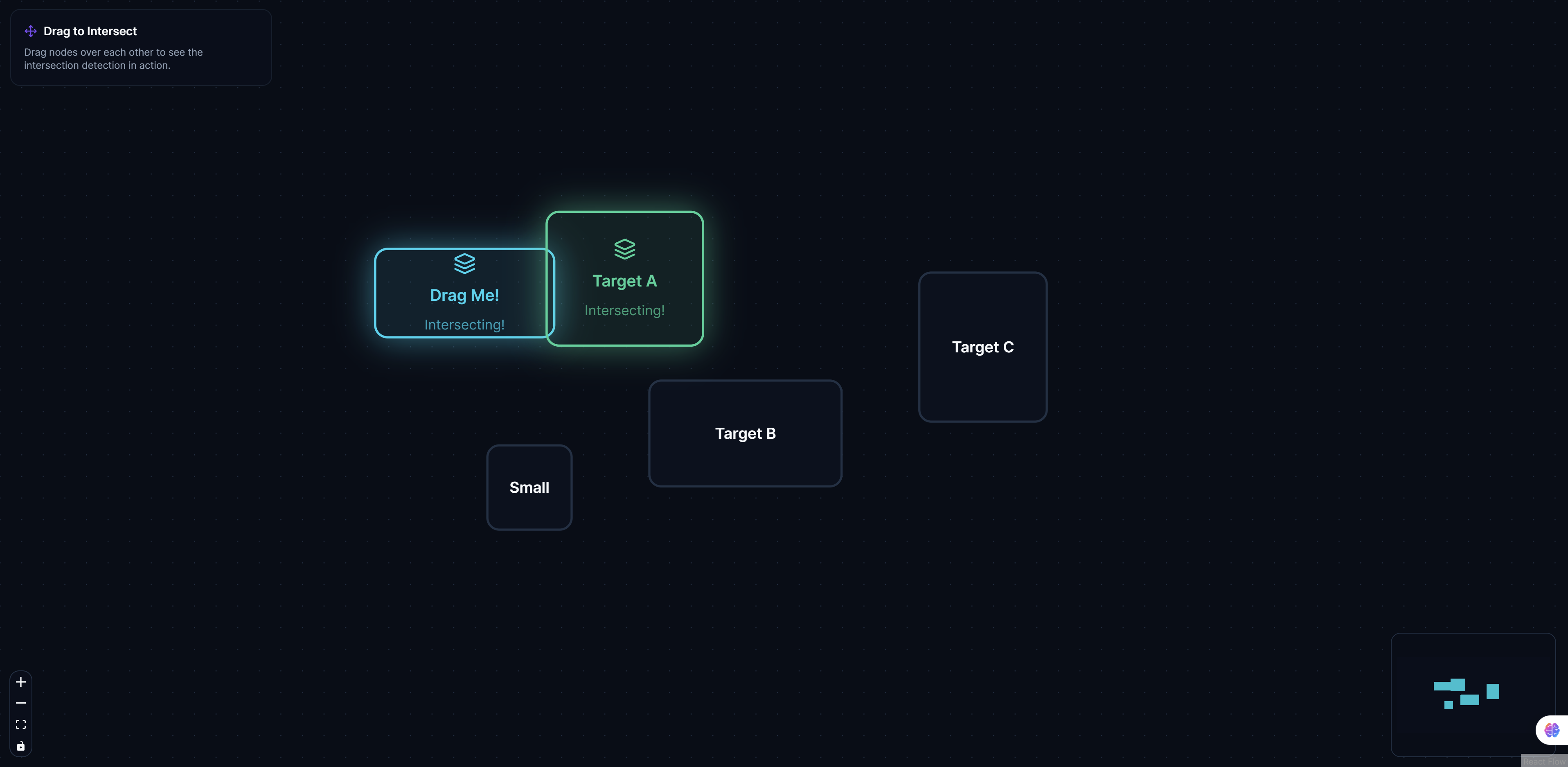
Node Intersections showcases advanced ReactFlow techniques for creating clean, professional diagrams with intelligent edge routing. This example solves one of the most common challenges in diagramming: how to draw connections between nodes without creating visual clutter or confusion.
The Challenge of Edge Routing
When building complex diagrams with many nodes and connections, edges can easily:
- Overlap nodes: Edges passing through nodes create visual confusion
- Create tangles: Multiple edges crossing create unreadable webs
- Obscure information: Important nodes get hidden behind edge crossings
- Reduce clarity: Visual clutter makes diagrams difficult to understand
Traditional diagramming tools often require manual edge routing, which is time-consuming and error-prone. ReactFlow Node Intersections demonstrates automated solutions that handle these challenges intelligently.
Key Features
Intelligent Edge Routing
The system automatically routes edges around nodes using sophisticated algorithms:
- Path finding: Calculates optimal paths that avoid node intersections
- Bend points: Adds intermediate points to route around obstacles
- Smooth curves: Creates visually appealing curved paths
- Minimal crossings: Reduces edge crossings for better readability
Collision Detection
Advanced collision detection identifies when edges intersect with nodes:
- Real-time detection: Continuously monitors for intersections
- Precise calculations: Uses geometric algorithms for accurate detection
- Performance optimized: Efficient algorithms handle large diagrams
- Multiple node shapes: Supports various node shapes and sizes
Path Optimization
The routing system optimizes paths to:
- Minimize length: Creates shortest possible paths
- Reduce crossings: Minimizes edge-to-edge crossings
- Maintain clarity: Keeps diagrams readable and organized
- Balance aesthetics: Creates visually pleasing layouts
Custom Routing Algorithms
Flexible routing system supports:
- Orthogonal routing: Routes edges using only horizontal and vertical segments
- Curved routing: Uses smooth curves for natural-looking paths
- Manhattan routing: Grid-based routing for technical diagrams
- Custom algorithms: Implement your own routing strategies
Performance Optimization
Efficient algorithms handle:
- Large diagrams: Supports diagrams with hundreds of nodes
- Real-time updates: Updates routing as nodes move
- Smooth interactions: Maintains performance during user interactions
- Scalable architecture: Handles increasing complexity gracefully
Implementation Details
Collision Detection Algorithm
The collision detection system uses geometric calculations:
// Example: Check if edge intersects with node
function edgeIntersectsNode(edge, node) {
const edgeStart = { x: edge.sourceX, y: edge.sourceY };
const edgeEnd = { x: edge.targetX, y: edge.targetY };
const nodeBounds = {
left: node.position.x,
right: node.position.x + node.width,
top: node.position.y,
bottom: node.position.y + node.height,
};
// Check if edge line segment intersects node rectangle
return lineIntersectsRect(edgeStart, edgeEnd, nodeBounds);
}
function lineIntersectsRect(start, end, rect) {
// Check if line segment intersects any edge of rectangle
const edges = [
[{ x: rect.left, y: rect.top }, { x: rect.right, y: rect.top }], // Top
[{ x: rect.right, y: rect.top }, { x: rect.right, y: rect.bottom }], // Right
[{ x: rect.right, y: rect.bottom }, { x: rect.left, y: rect.bottom }], // Bottom
[{ x: rect.left, y: rect.bottom }, { x: rect.left, y: rect.top }], // Left
];
return edges.some(edge => linesIntersect(start, end, edge[0], edge[1]));
}
Path Finding Algorithm
The routing algorithm finds optimal paths:
// Example: Find path avoiding nodes
function findPath(source, target, nodes) {
const obstacles = nodes.map(node => ({
x: node.position.x,
y: node.position.y,
width: node.width,
height: node.height,
}));
// Use A* or similar algorithm to find path
const path = aStarPathfinding(source, target, obstacles);
// Smooth the path
return smoothPath(path);
}
function smoothPath(path) {
// Remove unnecessary waypoints
// Convert to smooth curves
return path.map((point, index) => {
if (index === 0 || index === path.length - 1) {
return point;
}
// Calculate smooth curve control points
return calculateBezierControlPoints(path[index - 1], point, path[index + 1]);
});
}
Edge Routing Configuration
Configure routing behavior:
// Example: Routing configuration
const routingConfig = {
algorithm: 'orthogonal', // 'orthogonal', 'curved', 'manhattan'
spacing: 20, // Minimum distance from nodes
smoothing: true, // Smooth curves
avoidNodes: true, // Avoid node intersections
minimizeCrossings: true, // Reduce edge crossings
gridSize: 10, // Grid size for Manhattan routing
};
Use Cases
System Architecture Diagrams
Create clean architecture diagrams:
- Component relationships: Show how components connect
- Data flow: Visualize data flow between systems
- Service dependencies: Map service dependencies clearly
- Infrastructure diagrams: Document infrastructure layouts
Network Topology Visualization
Visualize network structures:
- Network maps: Show network device connections
- Topology diagrams: Document network topology
- Connection mapping: Map network connections
- Troubleshooting: Identify connection issues visually
Technical Documentation
Enhance technical documentation:
- API documentation: Show API relationships
- System documentation: Document system architecture
- Process documentation: Visualize technical processes
- Design documentation: Document design decisions
Database Schema Visualization
Visualize database structures:
- Entity relationships: Show table relationships
- Schema diagrams: Document database schema
- Foreign keys: Visualize foreign key relationships
- Data flow: Show how data moves through database
Process Flow Diagrams
Create process visualizations:
- Workflow diagrams: Document workflows clearly
- Business processes: Visualize business processes
- Decision trees: Show decision points and paths
- State machines: Visualize state transitions
Best Practices
Node Placement
- Strategic positioning: Place nodes to minimize edge crossings
- Group related nodes: Keep connected nodes close together
- Maintain spacing: Leave sufficient space between nodes
- Consider flow: Position nodes to show logical flow
Edge Routing
- Use consistent routing: Apply same routing style throughout diagram
- Minimize crossings: Arrange nodes to reduce edge crossings
- Group parallel edges: Route parallel edges together
- Highlight important edges: Use styling to emphasize key connections
Performance Considerations
- Limit node count: Keep diagrams manageable in size
- Optimize rendering: Use virtualization for large diagrams
- Cache calculations: Cache routing calculations when possible
- Progressive loading: Load and route edges progressively
Visual Design
- Clear node boundaries: Ensure nodes are clearly defined
- Distinct edge styles: Use different styles for different edge types
- Appropriate spacing: Maintain consistent spacing throughout
- Color coding: Use colors to distinguish edge types
Advanced Techniques
Dynamic Routing
Update routing as nodes move:
// Example: Update routing on node move
function onNodeDrag(nodeId, newPosition) {
const node = nodes.find(n => n.id === nodeId);
node.position = newPosition;
// Recalculate routes for affected edges
const affectedEdges = edges.filter(
e => e.source === nodeId || e.target === nodeId
);
affectedEdges.forEach(edge => {
edge.path = findPath(edge.source, edge.target, nodes);
});
updateDiagram({ nodes, edges });
}
Custom Routing Strategies
Implement custom routing algorithms:
// Example: Custom routing strategy
function customRouter(source, target, obstacles) {
// Your custom routing logic
// Could use:
// - Genetic algorithms
// - Force-directed routing
// - Grid-based pathfinding
// - Machine learning models
return optimizedPath;
}
Edge Bundling
Group similar edges together:
// Example: Edge bundling
function bundleEdges(edges) {
// Group edges with similar paths
const bundles = groupSimilarEdges(edges);
// Route bundles together
bundles.forEach(bundle => {
const bundlePath = calculateBundlePath(bundle);
bundle.edges.forEach(edge => {
edge.path = adjustToBundle(edge.path, bundlePath);
});
});
}
Benefits
Improved Readability
- Clear connections: Edges don't obscure important information
- Reduced clutter: Automatic routing reduces visual clutter
- Better comprehension: Cleaner diagrams are easier to understand
- Professional appearance: Polished, professional-looking diagrams
Time Savings
- Automatic routing: No manual edge positioning required
- Real-time updates: Routing updates automatically as diagram changes
- Consistent quality: Automated routing ensures consistent results
- Reduced errors: Fewer manual errors in edge placement
Scalability
- Handle complexity: Supports diagrams with many nodes and edges
- Performance: Efficient algorithms maintain performance
- Flexibility: Adapts to different diagram types and requirements
- Extensibility: Easy to extend with custom routing strategies
User Experience
- Smooth interactions: Routing updates smoothly during interactions
- Visual feedback: Clear visual indication of routing changes
- Intuitive behavior: Routing behaves as users expect
- Customization: Users can adjust routing parameters
Conclusion
ReactFlow Node Intersections demonstrates how advanced algorithms can solve real-world diagramming challenges. By automatically handling edge routing and collision detection, this example enables developers to create clean, professional diagrams without manual intervention.
The combination of intelligent routing algorithms, collision detection, and path optimization creates a powerful tool for building complex visualizations. Whether you're documenting system architecture, visualizing network topology, or creating technical diagrams, intelligent edge routing ensures your diagrams remain clear and readable.
Start building cleaner diagrams today and discover how intelligent edge routing can transform your visualizations.